Infrared Heating Technology – Different Types and How it Works

What is Infrared Technology?
Infrared radiation is the electromagnetic waves that are just beyond our visibility level on the electromagnetic spectrum. There are other types of invisible electromagnetic waves around us that are between 700 nanometers and 1-millimeter wavelength. Other electromagnetic waves are radio, gamma rays, x-rays, visible light and ultraviolet.
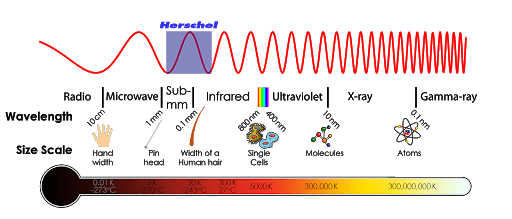
Infrared radiation rays can’t pass through hard objects like walls and it requires a line of sight. Infrared technology is becoming mainstream in our daily lives in recent years. It has many utilities including data transmission ability. However, since it requires a line of sight, IR is used for short distance settings. But infrared radiation data transmission is more secure than other types of wireless communication and it is very much hard to break through a well engineered infrared communication setting. Few examples of using infrared rays for data transmission purposes are Tv remote or other remote control systems that require a clear line of sight, cordless microphones and many more.
One of the popular applications of infrared radiation technology is its usage in heat transfer mechanisms. Infrared rays have the ability to transfer thermal energy. The temperature output is dictated by the peak wavelength of the infrared ray that is emitted. There are many usages of infrared radiation technology in heating process ranging from industrial steel, ceramic cuttings to regular household heaters.
Infrared Heating Process
Many of us would wonder about how does infrared heater work thinking that it must be a sophisticated technology that requires a vast amount of technical knowledge to understand. But you may be surprised to know that infrared heating process is the most common and abundant one in our nature. Yes, this is true. Our natural heater “The Sun” is heating our earth constantly from the beginning of time with this infrared heating process. The sun emits half of its energy by infrared radiation. To understand the infrared heating process lets begin with very basics of heat transferring mechanism.
Heat can be transferred in three ways. They are:
- Conduction: Conduction heating happens when two objects come in contact with different temperatures. Heat transfers from a warmer object to cooler object by the collision of molecules. Warmer objects have faster moving molecules and cooler object have slower moving molecules. Faster molecules give up some of their energy to slower molecules when they collide. Solid objects are best suitable for this kind of heat transfer.
- Convection: Convection heat transfer happens in case of gas and liquid objects. In the convection process, warmer gas or liquid molecules rise up to the place of cooler molecules and cooler molecules take place of the warmer molecules which have risen up. This constitutes a continuous cycle of air or liquid circulation which ultimately transfers the heat. Fan heaters are forced convection heaters that work this way.
- Radiation: Radiation is an energy transferring process in which no mass or medium is required to transfer the heat. Thermal radiation or infrared radiation is one kind of electromagnetic waves that passes in the speed of light. Radiation is emitted when highly energized electrons of high atomic levels fall down to lower atomic levels. All the objects around us, including our bodies emit and absorb radiation. Objects absorb radiation from high energized objects and emit radiation to objects that have low energized electrons. If the absorbing rate of an object is higher than its emitting rate the temperature of the object raises. Similarly, if the absorbing rate is lower than its emitting rate the temperature falls.
How Does Infrared Heating Work?
Infrared heating works in the radiation method. Unlike conventional heaters (electric space heaters or oil heaters), infrared heaters don’t require air to heat up, as a medium to transfer the heat to the targeted objects.
It is easy to understand the infrared heating process if we take the Sun as an example of the infrared heat emitter. The sun emits infrared ray to earth and other planets since, the atomic level of the sun is much higher and it has highly energized electrons. This energy is generated through gas combustion in the sun’s atmosphere. Radiation is emitted by the sun via infrared and ultraviolet ray as these highly energized electrons is absorbed by earth’s surface and other objects on it. This is the reason why we get warm even if the air is cold during winter. The earth then transfers the heat into our atmosphere through conduction or convection.
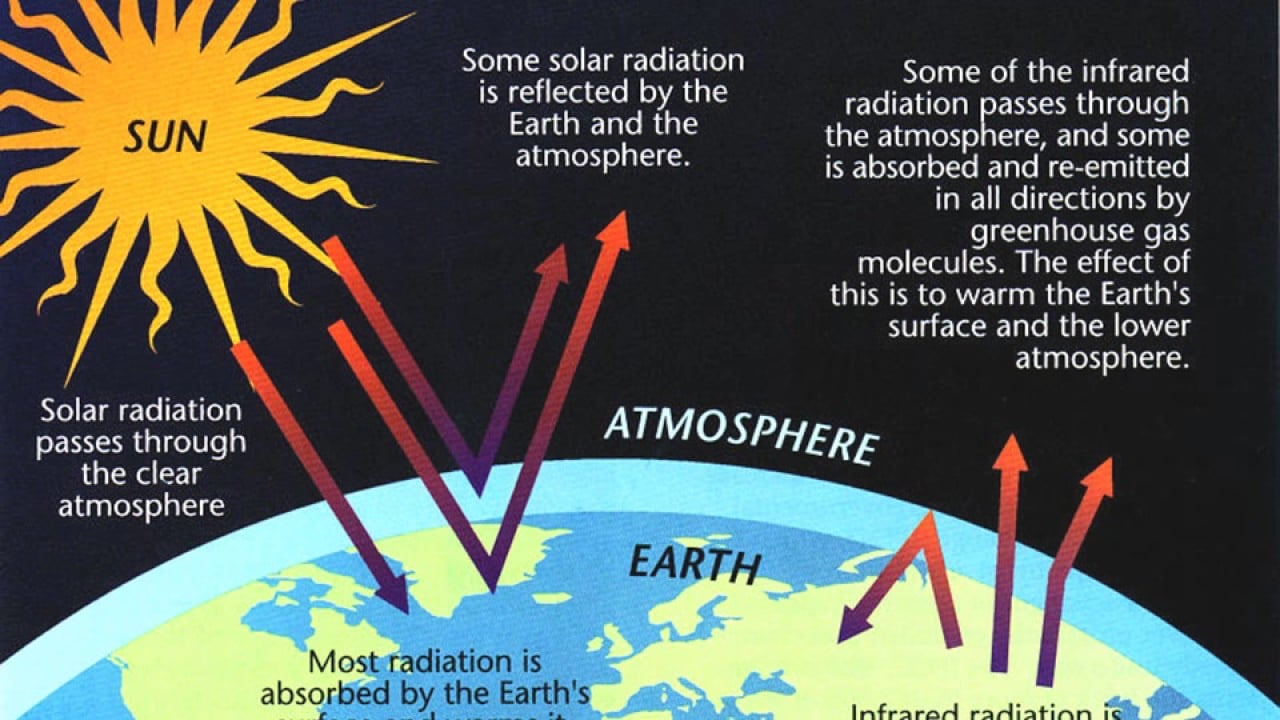
Infrared heaters work similarly. The energy is generated in an infrared heater through electricity, gas combustion or other types of fuel. Then, the heat is directed to an infrared heating panel which consists of ceramics or quartz tube or quartz lamp or metal sheath. The infrared panel then radiates the heat energy to its surrounding objects through infrared. The peak of this electromagnetic waves determines the degree of the temperature being transferred. It can vary from 0.7 microns to 300 microns. The shorter the wavelength, the higher the temperatures.
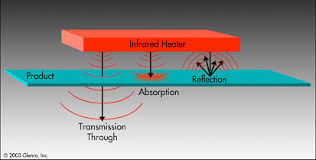
Types of Infrared Heater
On the basis of the radiated electromagnetic wavelength, infrared heaters are classified into three types. They are:
- Near Infrared Heater:
Near-infrared heaters have the lowest electromagnetic wavelength. They operate between 0.7 microns to 1.4 microns. Their intensity of heat is significantly higher than other types of infrared heaters. They generate approximately up to 1300°C temperatures. Near-infrared heaters are only used in industrial machines to cut steel and shape glasses.
- Medium wave Infrared Heater:
Medium wave infrared heaters operate in between 1.4 to 3 microns and they can generate 500°C to 800°C temperatures. Medium wave infrared is widely used in heat-seeking missile system all over the world and some other medical machine for medical purposes. For comfort heating, near infrared and medium wave infrared haters should not be used since their heat have burning risk if exposed for a long time.
- Far Infrared Heater:
Far infrared heaters have the longest electromagnetic wavelength. They operate in 3 or above microns and emit around 100°C temperatures. They are best suitable for comfort heating and thus widely used in residential buildings.
How Our Body Absorbs Infrared Heat
Since the Sun provides 50% of its energy through infrared radiation, our skin is naturally designed to absorb the infrared heat. However, different types of infrared radiation have different transmissive and absorption ability. It is important to know the difference before providing any blanket judgment.
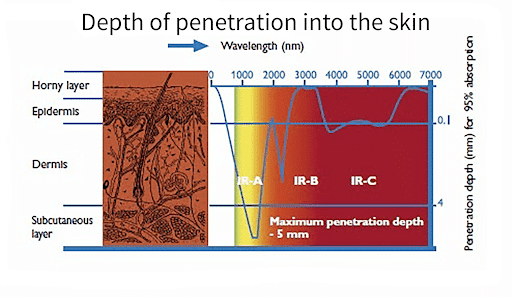
Near-infrared classified as IR-A has the most transmissive but least absorbing heat. This type of heat can penetrate our inner organs which may be fatal if exposed for a long time. Medium wave infrared classified as IR-B has less transmissive heat than near infrared. But the absorption rate is higher than that of near-infrared. On the other hand, far infrared has the least transmissive ability which can penetrate underneath our skin. But the absorption rate of far infrared is much higher than other types of infrared ray.
Is Infrared Heating Technology Efficient?
After understanding how does infrared heating work, we can easily assess the efficiency of infrared heaters. Infrared room heaters are the most prevalent comfort heaters on the market. There are many advantages to using infrared heaters.
- Direct Heating: Infrared heaters use radiation process to transfer the heat. That’s why they don’t need to heat up the air to transfer heat to the target objects. This feature makes it use minimal energy to get the optimal result.
- Less Green-house Gas Emission: Most of the infrared heaters work on electricity and they are around 85% efficient on transferring heat energy. This heat energy conversion rate is much higher than conventional heaters. Unlike gas burning central heating system, it has a positive effect on less greenhouse gas emission.
- No Odor: Infrared heaters don’t produce any toxins or pollutants as by-products of the heating process. As a result, unlike other typical heaters, they don’t produce any odor.
- Limited Harmful Particles: Since infrared heaters don’t need to heat up the air there is no unnecessary movement of air molecules in the room. It limits down the movement of harmful particles in the air.
- Swift in Heating: Infrared heaters can heat objects directly without needing any mass or medium. They don’t require the time to heat up the air molecules to transfer heat. That’s why it is very swift in heating comparing to other conventional heaters.
The infrared heating system is very efficient since it follows a very effective strategy named as, “Bio-Mimicry” (design or process modeled on any natural entities). This type of heating process is best for getting optimal utility with minimal energy which is crucial to our earth’s environmental sustainability.
Categorised in: Heaters















